What is the DIN standard for the destruction of data carriers? It gives you the framework for closed process protection. It consists of 3 parts: DIN 66399-1, DIN 66399-2 and DIN 66399-3.
In accordance with the European DIN 66399 standard and corresponding protection class, it is decisive which criteria the entire process must meet.
Below we would like to explain this DIN 66399 class using a diagram. The following diagram is a representation of the 3 different protection classes. The higher the protection class(number), the more sensitive the data on the data carrier. Sensitive data is secret data that poses a serious risk in the event of a data breach.
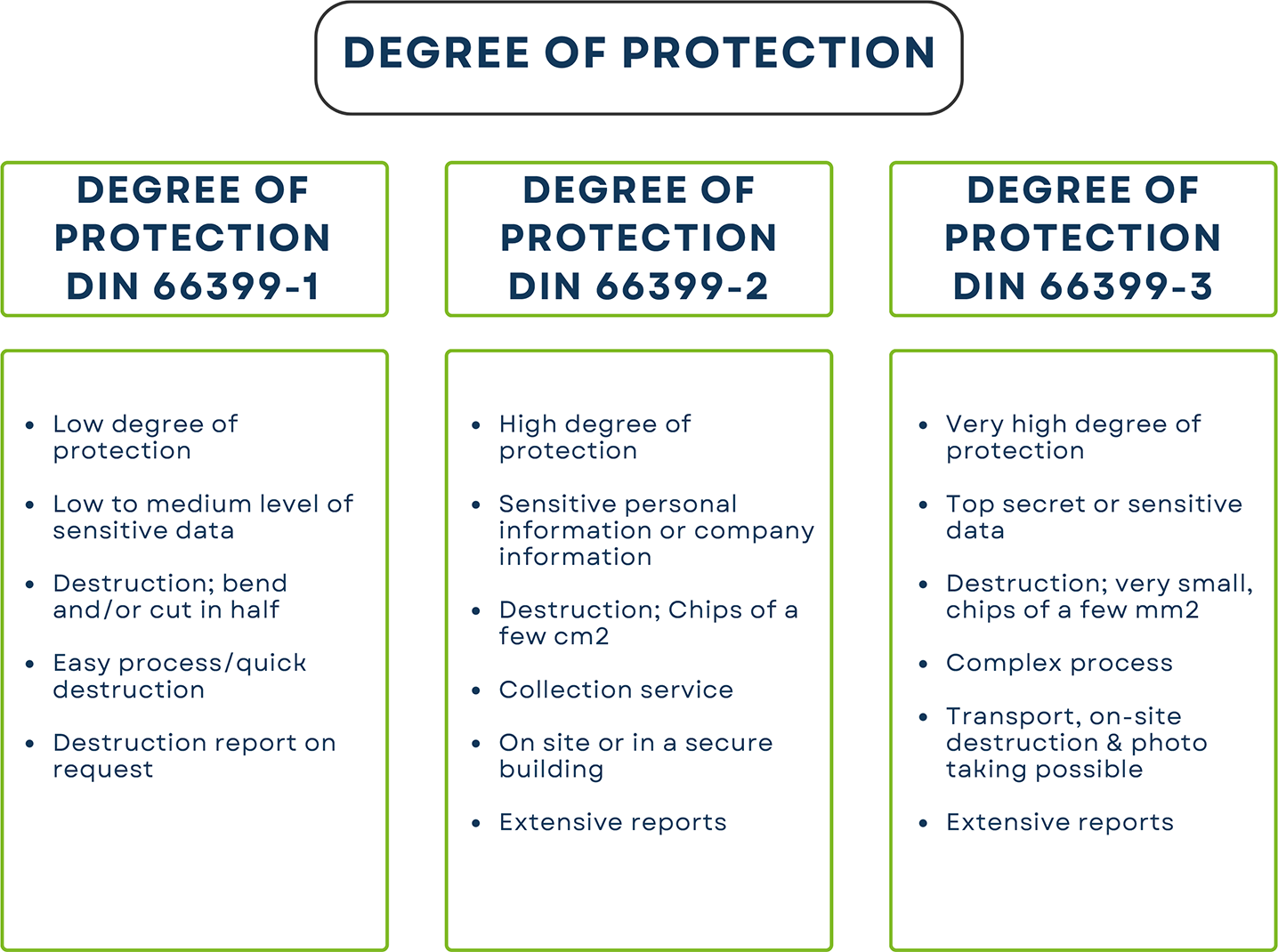
Once you have determined which protection class the data on the data carrier falls under, you can read exactly which destruction is associated with this degree in the overview below.
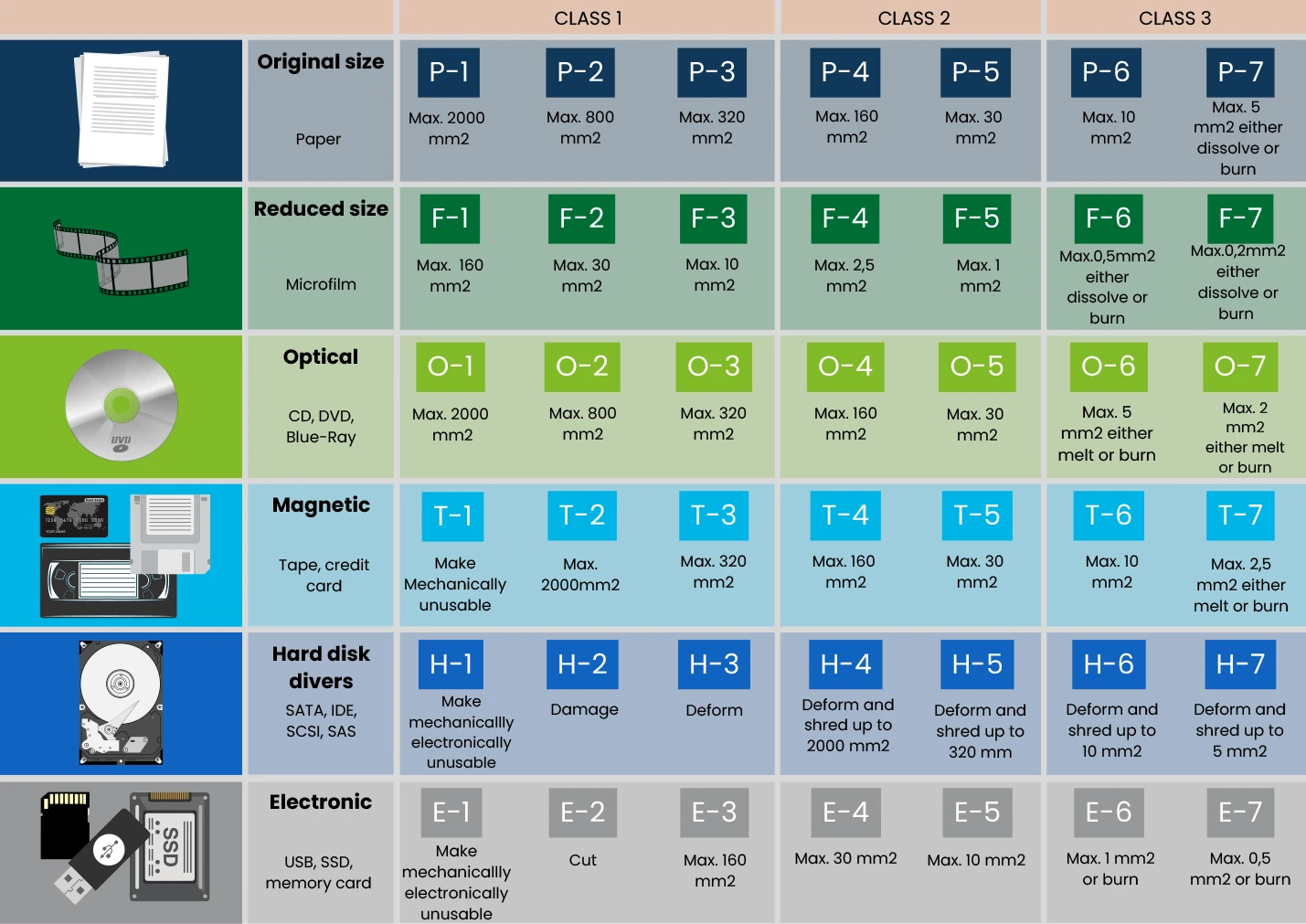
Security levels 1 to 7. The higher the level, the smaller the remaining fragments, depending on the type of data carrier. 7 is so small that it is impossible for the data to be read and fall into the wrong hands, therefore it is important to physically destroy this confidential information (hybrid and) according to the DIN 66399 standard. Depending on the type of data carrier/material category, (this is indicated with a letter before the number), together indicate the security level.
In the table above we have shown which 3 protection classes there are, but which safety level belongs to the protection class?
Protection class 1 – normal degree of protection
- General data
- Security level 1, 2 & 3
Protection class 2 – high degree of protection
- Confidential data
- Security level 4 & 5
Protection class 3 – very high degree of protection
- Confidential data/secret (top secret) data
- Security level 6 & 7
ISO certificates
ISO certificates are of crucial importance in order to comply with the DIN standard and processes for secure data destruction. Companies that work within the scope of, for example, ISO 9001, 14001, 27001 certificates can demonstrate that all processes meet these requirements. Which are audited annually by an independent auditor. ISO 9001 describes the management system, ISO 14001 is solely intended for the environment, ISO 27001 relates to data security in the broadest sense. With the combination of all 3 certificates and the annual external audit involved, a data destruction company can have sufficiently secured the data destruction process.
WEEELABEX compliant recycling
In order to comply with the legal requirements for waste in the form of electrical and electronic devices, also known as e-waste, you can choose a partner who works according to the WEEE guidelines. The abbreviation stands for; “Waste of Electric and Electronic Equipment”. This guideline has been incorporated into Dutch legislation. Complete transparency about what happens to the equipment and how the electronic waste or e-waste is recycled.
Extensive Destruction Statement
After destruction, a complete and extensive report is often drawn up. You will usually receive this comprehensive declaration of destruction immediately after destruction. The reports are proof that the data has been removed correctly. The reports contain all relevant information relating to the destroyed data carriers. Do you work within the scope of ISO certification yourself? In that case, reporting with a declaration of destruction during an ISO audit may be a requirement.